
Autonomous vehicles have long promised to redefine how we move, but the rise of robotaxis signals that this future is finally materializing—and fast.
What was once confined to R&D labs and speculative timelines is now hitting real streets in major U.S. cities and parts of China.
With ride-hailing giants, automakers, and tech titans racing to commercialize driverless mobility, the stage is set for a major disruption in transportation and an explosive new chapter in investing.
The economic incentive is compelling: robotaxis offer the potential to slash operating costs, remove human error, and unlock entirely new business models in mobility-as-a-service.
At the same time, rapid advancements in AI, sensors, and compute power are compressing the timeline to mainstream adoption.
Investors who understand the evolving landscape—and can separate hype from durable progress—stand to gain from what may be one of the most transformative trends of the next decade.
This article explores the current state of the robotaxi market, the key players shaping the space, and the most promising ways to position your portfolio for long-term exposure.
Contents
The robotaxi market represents one of the most compelling investment opportunities in the mobility sector, driven by fundamental inefficiencies in current transportation models and rapidly maturing autonomous vehicle technology.
What was once science fiction is now approaching commercial reality, with early market leaders already demonstrating operational viability at scale.
Industry analysts project explosive growth for the robotaxi sector, though estimates vary significantly based on adoption assumptions and geographical scope.
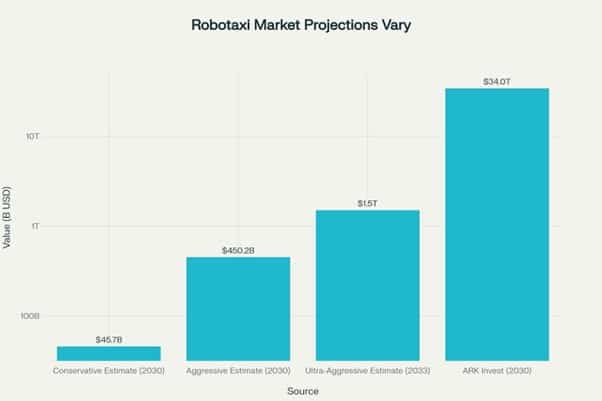
The global robotaxi market, valued at USD 0.4 billion in 2023, is expected to reach USD 45.7 billion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 91.8%.
More aggressive projections suggest even larger opportunity sizes, with some forecasts expecting the market to reach USD 450.2 billion by 2033, from USD 1.7 billion in 2023, growing at a CAGR of 74.7%.
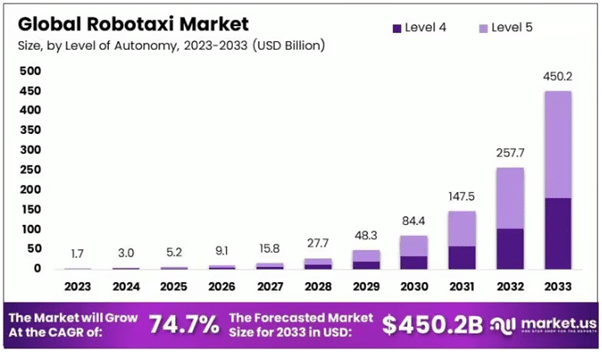
The wide range in these projections—spanning from $45 billion to over $4 trillion depending on the timeframe and methodology—reflects both the nascent nature of the market and the transformative potential of autonomous mobility.
These estimates encompass not just ride-hailing services but the broader autonomous transportation ecosystem, including logistics, delivery, and mobility-as-a-service applications.
The robotaxi landscape is rapidly consolidating around a few key players with demonstrated operational capabilities.
Waymo dominated the U.S. robotaxi market in 2024, with expansion plans for 2025 focusing on more cities and continuing R&D on newer technology.
The company’s operational momentum is impressive: Waymo reached 10 million robotaxi trips, doubling in five months, demonstrating both consumer acceptance and scalable operations.
Tesla represents the primary challenge to Waymo’s leadership, with CEO Elon Musk arguing for a fundamentally different approach to market capture.
Musk stated “Teslas probably cost a quarter, 20%, of what a Waymo costs and made in very high volume.
I don’t see anyone being able to compete with Tesla at present.”
This cost advantage claim centers on Tesla’s vision-only approach versus Waymo’s sensor-heavy strategy, potentially offering a path to mass market deployment.
However, the competitive landscape remains fluid and challenging.
Tesla faces a big challenge in surviving its safety test, as other companies like Uber’s self-driving unit and GM’s Cruise could not overcome high-profile accidents.
The recent market reset, with GM’s exit resetting the robotaxi race, with Waymo’s proven leadership and Tesla’s bold ambitions setting the stage for intense competition, has clarified the field but also highlighted the operational complexity of autonomous vehicle deployment.
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/how-waymo-got-the-edge-on-the-competition-and-teslas-robotaxi-so-far-090019552.html
The robotaxi industry’s journey has been marked by remarkable achievements alongside sobering setbacks, providing crucial lessons for investors evaluating this space.
Understanding both sides of this story is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Proven Commercial Success Stories
Waymo’s trajectory demonstrates the viability of robotaxi operations at scale.
The company achieved 10 million rides by May 2025, with Swiss Re data showing 88% fewer property damage claims and 92% fewer bodily injury claims compared to human drivers.
This safety record, combined with rapid service expansion, validates the commercial model for well-executed robotaxi operations.
Robotaxi Success: Tesla Defies Critics with Smooth Autonomous Rides
Despite operational challenges, Tesla’s Austin launch triggered a 9% stock surge, adding nearly $100 billion in market value.
This demonstrates significant investor confidence in the vision-only approach, even as the company works through early deployment issues.
Meanwhile, Baidu’s Apollo Go has surpassed 11 million rides across 15 cities with over 1,000 driverless vehicles, successfully validating business models in price-sensitive markets.
Critical Failures and Cautionary Tales
The most dramatic failure occurred when GM completely shuttered Cruise in February 2025 after investing $9 billion.
The decision followed a devastating pedestrian dragging incident and subsequent regulatory issues, highlighting how quickly public trust and regulatory approval can evaporate.
This collapse serves as a stark reminder that technological capability alone doesn’t guarantee commercial success.
Tesla’s Robotaxi Stumbles on Launch Day as Safety Concerns Emerge During Pilot Launch
Tesla’s operational challenges have been well-documented, with Reuters verifying at least 11 videos showing concerning behaviors, including vehicles entering oncoming traffic lanes and dropping passengers in intersections.
The industry has also faced sobering realities with fatal incidents, including Tesla’s first pedestrian fatality in 2023 and Waymo’s involvement in San Francisco’s first driverless vehicle fatal collision in January 2025.
Understanding the fundamental economics of robotaxis versus traditional ride-hailing illuminates why this transition represents such a compelling investment opportunity.
The elimination of driver compensation, which accounts for 70-75% of traditional ride-hailing costs, allows robotaxi operators to potentially offer lower prices while maintaining higher margins.
However, this advantage comes with trade-offs. Robotaxis face significantly higher vehicle costs due to expensive sensor technology and increased technology operations expenses.
The cost allocation shifts dramatically: approximately 60-65% goes to vehicle costs, 15-20% to technology operations, and 10-15% represents profit margins compared to traditional ride-hailing’s 5-7%.
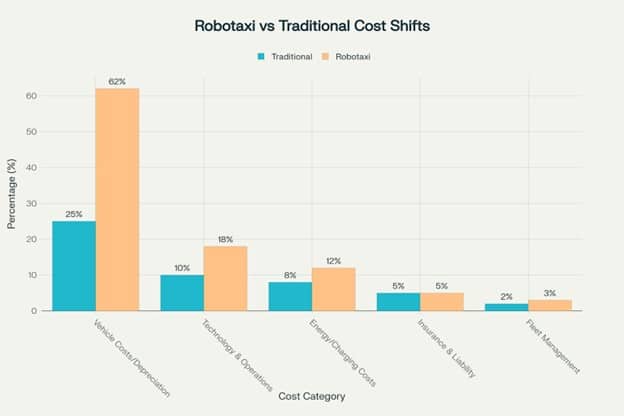
The key to profitability lies in utilization rates and cost-per-mile projections.
Some estimates suggest costs could drop to $0.30-$0.50 per mile by 2030, making robotaxis 40-60% cheaper than current ride-hailing services.
Vehicles operating at 65% utilization versus 30% can dramatically impact revenue per vehicle, potentially generating $500 billion in net income annually with 50 million vehicles at conservative utilization rates.
While basic ride fares provide the foundation, successful robotaxi operators are developing multiple revenue streams that could significantly enhance profitability.
This diversification strategy represents a crucial differentiator for investors evaluating long-term potential.
In-vehicle advertising presents immediate monetization opportunities, with captive audiences during rides.
Companies can leverage anonymized mobility data, selling insights to city planners, advertisers, and real estate developers.
Subscription models for premium services and B2B partnerships for corporate transportation needs offer additional recurring revenue streams.
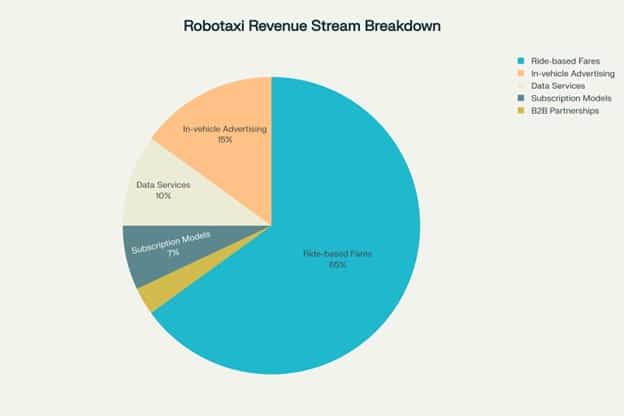
The data monetization opportunity is particularly compelling.
Robotaxis generate vast amounts of valuable information about traffic patterns, consumer behavior, and urban mobility trends.
This data, properly anonymized and packaged, represents a high-margin revenue stream that traditional transportation companies cannot match.
Early movers who establish data partnerships and develop analytics capabilities will likely capture disproportionate value as the market matures.
The path to widespread robotaxi deployment faces significant regulatory hurdles that could materially impact timelines and profitability.
Tesla’s recent Austin rollout revealed critical issues including speeding violations and lane deviations that triggered NHTSA investigations.
These challenges highlight the complex interplay between technological capability and regulatory compliance.
State-by-state regulatory variations create additional complexity.
Texas’s HB5426 law requires three years of supervised testing before unsupervised operations, while other states mandate varying insurance amounts from $1 million to $5 million for autonomous vehicle operations.
The Autonomous Vehicle Industry Association has called for unified federal frameworks, but progress remains slow.
The shift from driver-based to manufacturer-based liability represents a fundamental transformation in risk allocation.
Goldman Sachs projects that per-mile insurance costs could fall by over 50% by 2040, though premiums may initially climb due to high-tech vehicle repair costs and cyber vulnerabilities.
Companies like Tesla will likely need to offer their own insurance coverage, adding another layer of operational complexity.
While the U.S. market garners significant attention, international opportunities present equally compelling investment cases.
China, in particular, offers massive scale potential with government support for autonomous vehicle development.
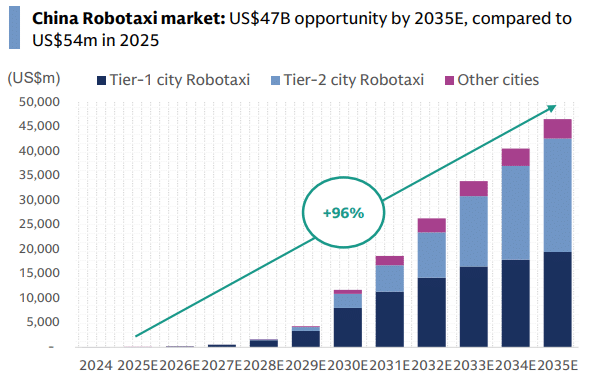
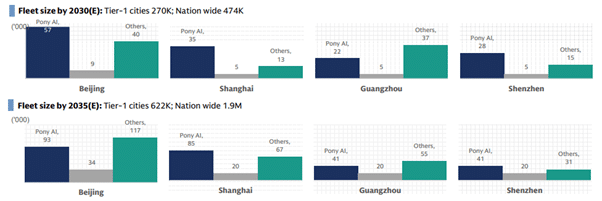
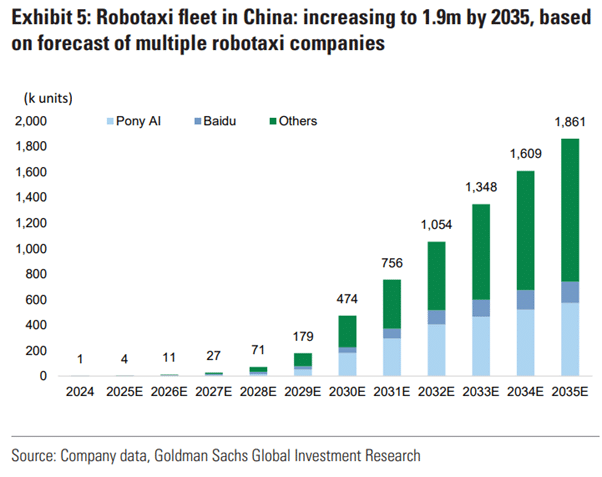
Goldman Sachs Research analysts believe that with 500,000 robotaxis expected to be operating across 10+ cities in China by 2030, the shifting the question from “if” to “how” companies will commercialize this technology.
Ford CEO Jim Farley recently said “It’s the most humbling thing I’ve ever seen,” speaking of his trips to China.
During an interview with the journalist Walter Isaacson, Farley said he’s been to China six or seven times in the past year to scope out the competition.
One of his big takeaways is the advanced tech in those vehicles.
“They have far superior in-vehicle technology,” Ford’s CEO said.
The deployment of robotaxi services requires substantial infrastructure investment beyond the vehicles themselves.
Essential components include high-definition mapping systems, specialized maintenance facilities, fleet management centers, and 5G connectivity infrastructure.
These requirements create investment opportunities in supporting industries.
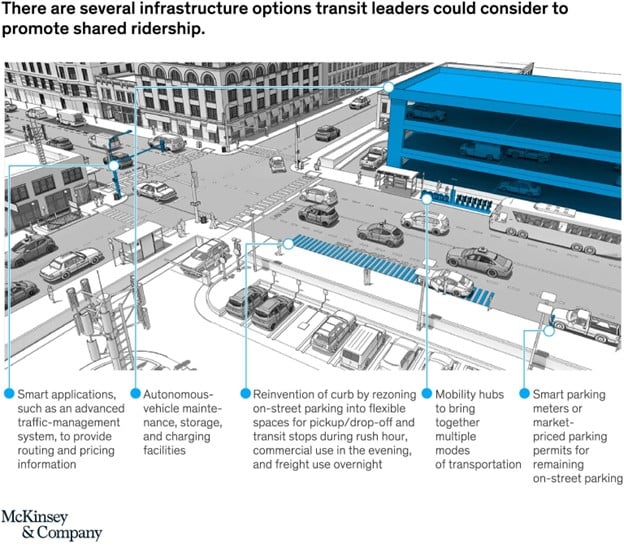
Cities must adapt their infrastructure with smart traffic management systems, flexible curb spaces for pickup and drop-off, and charging networks.
The mapping infrastructure alone represents significant ongoing costs, as companies must maintain real-time updates for construction, traffic patterns, and route optimization.
https://www.cnbc.com/2025/05/20/waymo-ceo-tekedra-mawakana-10-million.html
The robotaxi ecosystem presents multiple investment entry points, from direct operators to platform providers.
Some analysts suggest Uber represents the best company to benefit from the rise of autonomous taxis as a platform play rather than direct operator, highlighting the value of established marketplace dynamics and customer relationships.
This platform approach offers several advantages: lower capital requirements, reduced operational risk, and the ability to aggregate multiple autonomous vehicle providers.
Companies with established customer bases and sophisticated routing algorithms can potentially capture value without bearing the full cost of vehicle development and deployment.
Direct operators like Waymo and Tesla offer higher risk but potentially higher reward profiles. Success requires mastering complex technology, managing regulatory relationships, and building consumer trust.
The supply chain approach offers another angle, with companies like NVIDIA providing essential computing platforms and sensor manufacturers like Mobileye enabling the technology stack.
For investors seeking exposure without picking individual winners, several ETFs offer diversified robotaxi exposure.
The ARK Autonomous Technology & Robotics ETF (ARKQ), Global X Autonomous & Electric Vehicles ETF (DRIV), and Robo Global Robotics & Automation ETF (ROBO) provide varying approaches to the theme.
Consumer discretionary ETFs like XLY and VCR offer substantial Tesla exposure, benefiting from robotaxi developments while maintaining broader sector diversification.
When evaluating these vehicles, consider expense ratios, concentration risk, and whether the holdings align with your robotaxi investment thesis.
Some funds focus heavily on established automakers transitioning to autonomous technology, while others emphasize pure-play technology companies.
This Is The Best Robotaxi Stock To Buy
Based on current progress and regulatory realities, investors should calibrate expectations appropriately.
The World Economic Forum’s analysis suggests large-scale robotaxi deployments will remain limited to select global cities for the next decade.
Personal vehicles will likely remain dominated by L2 and L2+ systems through 2035, while L4 deployment stays niche during this timeframe.
This measured rollout creates opportunities for patient investors.
Early deployments in favorable regulatory environments will provide proof points for broader adoption.
Companies demonstrating consistent safety records and operational efficiency in initial markets will likely capture disproportionate value as the industry scales.
The key is identifying operators with both technological capability and operational excellence to navigate this complex transition.
The robotaxi revolution is not just a technological marvel; it’s a fundamental shift in transportation economics, infrastructure, and investment.
While the journey has been marked by both spectacular successes and sobering failures, the long-term direction remains clear.
As autonomous fleets begin to scale and cost curves fall, the financial opportunity tied to this transformation could be enormous.
But like all early-stage disruptions, success won’t be evenly distributed.
Some companies will lead, others will pivot, and many will disappear entirely.
The GM Cruise shutdown serves as a stark reminder that even well-funded efforts can fail spectacularly.
The key for investors is to approach the space with eyes wide open: understand the technology risks, regulatory hurdles, and operational complexities while maintaining exposure to the transformative potential.
Consider a diversified strategy that combines high-conviction direct plays with exposure to the broader ecosystem through enablers and ETFs.
Be patient, stay informed, and don’t underestimate the power of platform economics in this evolving landscape.
The winners may not be who you expect—remember that Uber, not a car manufacturer, might capture significant value simply by aggregating supply.
The robotaxi future is already rolling out on streets from San Francisco to Shenzhen.
The only question is: will you be along for the ride?
Trade safe!
Disclaimer: The information above is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as investment advice. The strategy presented would not be suitable for investors who are not familiar with exchange traded options. Any readers interested in this strategy should do their own research and seek advice from a licensed financial adviser.

